What is a PFMEA? Steps to conduct your PFMEA
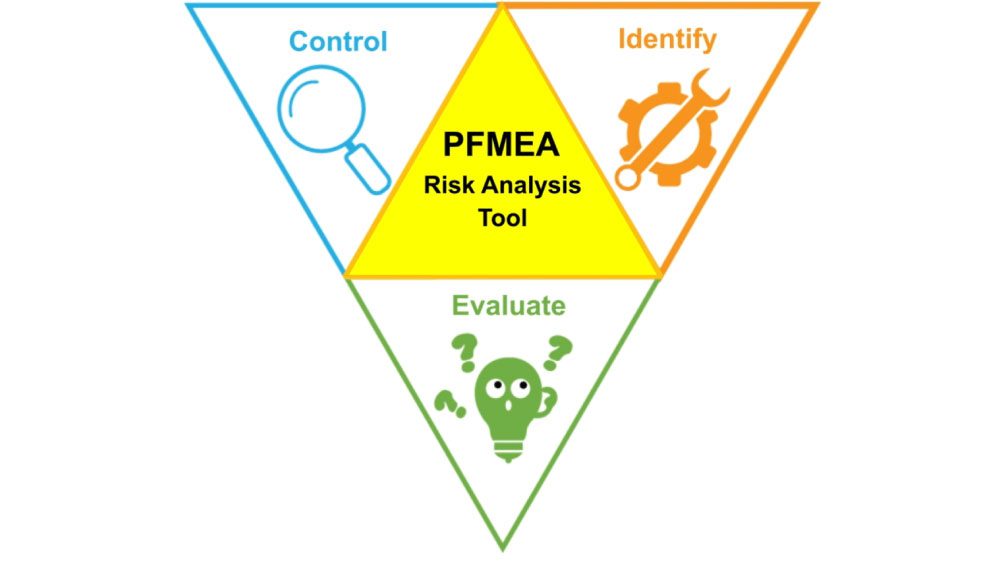
Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is the analytical approach used by companies, businesses, or cross-functional groups to identify and assess possible process failures.
PFMEA helps to determine the effect of the failure and to identify and prioritize the action items with the objective of reducing the risk. Documentation must begin prior to the product’s manufacturing and also update throughout its lifespan. It is widely used in engineering, and students usually need assignment help to complete PFMEA questions.
Evaluation criteria of PFMEA
For each process stage, PFMEA provides a score of one to 10 on a scale of one to ten.
- Severity— Failure modes rank from 1 to 10, each indicating how harmful they are to the system’s safety. A failure mode effect analysis, which evaluates the likelihood of a failure mode by splitting it down into sub-elements, may require in most situations for processes with severity ratings over eight.
- Occurrence— Using a scale from one to 10, it measures the likelihood of a failure occurring, with one being the lowest and 10 the most. To put it another way, a failure which occurs once every five years may get a score of one, and one every hour or minute would receive a score of ten.
- Detection— It determines the likelihood that a failure will be occurring, with one being the greatest likelihood and 10 being the lowest.
- Risk priority number (RPN)= severity*occurrence*detection. The rule of thumb is that any RPN value over 80 should be correct. The goal is to reduce the RPN number as a result of the remedial activity.
Steps to conduct your PFMEA
Follow these steps to learn how to conduct a PFMEA:
- A team leader should assemble a cross-functional group of the project owner and operational support staff.
- Ask the team leader to specify the PFMEA’s scope, objectives, and completion date.
- Make a copy of the PFMEA process map for each of the stages.
- As a group, assign severity, incidence, and detection ratings to each phase of the process.
- Recommend remedial measures for each phase of the process depending on the RPN value.
- Corrective measures must write on a RACI chart, which identifies who is accountable, responsible, consulting, and informing.
- Track remedial actions and modify the FMEA regularly by having the team leader.
- Keep track of changes in the process, design, and other significant findings that would validate and revise the PFMEA.
- The team leader should have regular meetings to go through the PFMEA. Quarterly reviews may be a possibility if the process is doing well.
Industries that follow PFMEA
- Automotive: Large-scale product recalls have to avoid because of the use of PFMEA in the automobile industry. Automobile manufacturers have also used PFMEA to increase their cars’ safety.
- Manufacturing: PFMEA is widely used in the manufacturing business, as previously stated. In order to avoid expensive repairs down the road, manufacturers depend on the technique. To avoid failing in their assignments, students usually search, “can someone do my assignment?”
- Healthcare: Historically, medical procedures haven’t placed much emphasis on accident prevention. However, many healthcare systems were not build to protect medical personnel from making terrible mistakes for whatever reason.
- Software Development: Focusing on removing technical flaws that result in shoddy software, unreliable user experiences, and expensive blunders is the goal of software FMEA.
Agriculture: PFMEA has been continuously in use for agriculture. Farmers may evaluate risks to product quality in terms of environmental factors, machinery, and production me